How shall we address the President?
August 31, 2009 by TimHughes · 2 Comments
Although we may think it odd today, back in 1789 when our federal government was just being formed and George Washington was inaugurated as America’s first President, there was little precedence as to how to address the new chief executive of the government. The only examples given by the European powers were royalty where “your highness” or “your excellency” were appropriate. But what about a democratically elected President?
The article shown is taken from the “Gazette of the United States” newspaper from New York, May 16, 1789, about two weeks after Washington was inaugurated. It provides some interesting insight in to the thoughts of the day when the government was truly in its infancy.

A novel way to keep the money coming…
August 29, 2009 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
 The following is taken from the “Gentleman’s Magazine” issue of July, 1768, published in London. Perhaps a distant ancestor of Edgar Allan Poe?
The following is taken from the “Gentleman’s Magazine” issue of July, 1768, published in London. Perhaps a distant ancestor of Edgar Allan Poe?
The “Carrier’s Address”…
August 27, 2009 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
Credit for portions of the following must be given to Clarence Brigham & his work “Journals & Journeymen”, as well as to the Bentley Historical Library at the University of Michigan.
 During the nineteenth century, newspaper carriers were often not paid by the publishers of the papers. They typically depended upon donations from patrons at the end of the year. To remind the public that the carriers depended on their donations, newspaper publishers issued poetic broadsides or booklets for New Years Day. These poems often recounted the major news stories of the previous year, but always closed with a plea to pay the carrier.
During the nineteenth century, newspaper carriers were often not paid by the publishers of the papers. They typically depended upon donations from patrons at the end of the year. To remind the public that the carriers depended on their donations, newspaper publishers issued poetic broadsides or booklets for New Years Day. These poems often recounted the major news stories of the previous year, but always closed with a plea to pay the carrier.
They were rarely saved since they contained no news reports and as a result are rather rare today. Although many Carriers’ Addresses were contained within the body of the first newspaper issue in the new year, the most sought after are the broadside editions, printed on one side of a sheet of paper typically with ornate lettering, decorative borders, etc. The more decorative the Address the more collectible. The “New York Weekly Museum” address for 1790 had an engraving of a boy delivering a paper at a doorway, one of just a few with such an illustration.
The earliest known examples were done for the “American Weekly Mercury” of Philadelphia in 1720, 1721 and 1723 although none have been found. The earliest located for the American Antiquarian Society is that of January 1, 1735. Benjamin Franklin included them in his “Pennsylvania Gazette” as early as 1739 (see photo).
The amount of the donation expected by the carrier was generally left to the customer. Many of the verses concluded with such a sentiment as “Remember the poor printer’s Devil” or “Be bounteous to the Printer’s boy”. Sometimes the sentiment was more definite, such as “I won’t Refuse a six pence” and “Please keep the cents and–give the silver”.
By the 1870’s the custom began to fall off, likely due to the beginning of more commercial & larger influential newspapers which considered such a custom undignified, also falling away in favor of the distribution of Christmas or New Year’s cards by the end of the 19th century. The latest located for the American Antiquarian Society is dated 1904.
What’s the best newspaper to have?
August 27, 2009 by TimHughes · 2 Comments
Most collectors of historic newspapers would agree that the best newspaper to have for an historic event is the city where it happened. Among the more notable would be the Boston Gazette reporting the Boston Massacre, the Honolulu issue on the bombing of Pearl Harbor, the Dallas newspapers on JFK’s assassination, and a Chicago newspaper covering the St. Valentine’s Day massacre. Stock market or finance related events are best in the Wall Street Journal, and when events happened in small towns which had no newspapers, the closest major city might be the next best thing.
But some events can’t be had—or can very rarely be had—from the city where “it” happened. What are the best issue in those situations? What’s the best issue for man landing on the moon? Or the atomic bomb dropping on Hiroshima & Nagasaki? Or the first manned flight around the earth? Or the discovery of the North Pole? Or Edison’s invention of the phonograph? What would be the best newspaper for the sinking of the Titanic?
 There are many answers; perhaps as many as there are collectors. But I’ll offer a few thoughts. Actually what brought all of this to mind was an issue I recently wrote up for a future catalog. It announced the dropping of the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and was from Knoxville, Tennessee. The headline reads: “Power Of Oak Ridge Atomic Bomb Hits Japs”. Keeping in mind that Oak Ridge, Tenn., the home of the Manhattan Project which developed the bomb, is less than 20 miles from Knoxville, it is not surprising that they localized the headline with mention of the role Oak Ridge played. I suspect no other newspaper in the country mentioned Oak Ridge in their headline on the atomic bomb drop. Outside of finding a Japanese newspaper from the day after, I suspect this Knoxville newspaper could be the best issue on this event.
There are many answers; perhaps as many as there are collectors. But I’ll offer a few thoughts. Actually what brought all of this to mind was an issue I recently wrote up for a future catalog. It announced the dropping of the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and was from Knoxville, Tennessee. The headline reads: “Power Of Oak Ridge Atomic Bomb Hits Japs”. Keeping in mind that Oak Ridge, Tenn., the home of the Manhattan Project which developed the bomb, is less than 20 miles from Knoxville, it is not surprising that they localized the headline with mention of the role Oak Ridge played. I suspect no other newspaper in the country mentioned Oak Ridge in their headline on the atomic bomb drop. Outside of finding a Japanese newspaper from the day after, I suspect this Knoxville newspaper could be the best issue on this event.
Any space flight issue might best be from the Cape Canaveral area. Or perhaps the hometown of one of the astronauts involved. We offer a Wapakoneta, Ohio, newspaper on man walking on the moon as it’s Neil Armstrong’s hometown, and their headline is localized by: “NEIL STEPS ON THE MOON” while most newspapers reported “MAN WALKS ON THE MOON”.
The graphic appeal of the front page is a major factor as well and in the eye of many is always the deciding factor in determining the “best” for that event. We price Titanic issues almost entirely on the “wow” effect of the front page, as the larger the headline and more dramatic the look the better, regardless of where the newspaper was printed. This holds true for many 20th century events, such as D-Day, V-E Day, V-J Day and and any other military event. Some might argue that the “Stars And Stripes” would be the best paper for a military event, or perhaps newspaper from Washington D.C., home of the Pentagon.
We’d like to hear what you think on the best issues for historic events which can’t be found from the city involved. I’m sure your thoughts will spark other collectors to refine their holdings with better or more appropriate newspapers for notable events. Let us here from you!
More on printing newspapers in the 1700’s…
August 24, 2009 by TimHughes · 3 Comments
This article is primarily taken from the April, 1996 edition of “Collectible Newspapers” edited by Rick Brown, whom we thank for this contribution. It offers some interesting insights into the printing & distributing of newspapers in the colonial and post-colonial era of the United States.
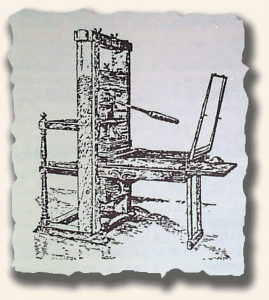 Newspapers from the latter half of the 18th century were relatively scarce. One factor was that early settlers were busy clearing the land & otherwise making the land habitable & sustaining. Plus only a small percentage of the population had reading skills beyond that of the basic rudiments. Although most towns of any size by 1715 had tracts of land set aside for schools, few actually had schools built & in operation.
Newspapers from the latter half of the 18th century were relatively scarce. One factor was that early settlers were busy clearing the land & otherwise making the land habitable & sustaining. Plus only a small percentage of the population had reading skills beyond that of the basic rudiments. Although most towns of any size by 1715 had tracts of land set aside for schools, few actually had schools built & in operation.
Nearly all 18th century newspapers were edited & published by printers that had a general printing business and also printed pamphlets, books, broadsides, lottery tickets, etc. Many also sold merchandise, groceries, patent medicines, and a variety of other goods. Rags, which were used to make the paper , were scarce in the colonies so most of the paper was imported from England.
Newspapers were printed on wooden hand presses with each applicatoin of ink to paper requiring a pull of by lever and screw. It was not until around 1816 that the new iron Columbian press came into general use. Instead of a screw it used a series of compound levers that multiplied the pull of the operator. But still, all hand presses were slow & laborious. The forms had to be laid by hand and the ink was poor and of uneven quality. Types were frequently old and worn.
After the newspapers were printed, distribution difficulties were encountered. Circulation was confined, for the most part, to the towns in which they were published. They were distributed to the rural areas by postboys on horseback and by stagecoach drivers. The roads were bad & the postal system was slow. Subscribers were few & the cost of an issue relatively expensive so newspapers were typically handed around from one to another so that a single copy was ready by many. Even those who subscribed often failed to pay for their subscriptions.
It has been estimated that the largest circulation of a single newspaper during the earlier colonial period was about 350 and that only a few reached this high of a number of circulation. By the 1750’s circulation for larger city newspapers reached upwards of 600 of each issue printed and during the Revolutionary War some newspapers boasted circulations in excess of 2000. By 1790 most newspapers were printing less than 1000 copies but the very popular “Columbian Centinel” from Boston was printing over 4000 copies of each printing date.
Despite poor equipment, limited circulation, nonpaying subscribers, poor distribution facilities & the general unprofitability of publishing a newspaper, the number of newspapers being published continued to increase as the years went by. There were numerous failures, but new newspapers were established to replace them. From 1704 to 1820 about 1634 newspapers came to life and died. Of that number only two-thirds of them lived beyond three years.
Beware of the pony…
August 22, 2009 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
 I suspect this little item printed in “The Sag Harbor Express” newspaper from Long Island, New York on February 23, 1871 is fictitious, but it gives a sense of 19th century humor nonetheless.
I suspect this little item printed in “The Sag Harbor Express” newspaper from Long Island, New York on February 23, 1871 is fictitious, but it gives a sense of 19th century humor nonetheless.
My Collecting Story… David Cunningham…
August 20, 2009 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
 I started collecting newspapers about 2-3 years ago. Originally I collected US coins and baseball cards but transitioned to picture postcards from the early 1900’s. I wanted to go back further in time so I started to collect letters/stampless letters from the 1800’s including a few neat letters from the Civil War. In my quest to find earlier documents I stumbled upon your rarenewspaper website. I was amazed that newspapers could be had from the 1600/1700’s. Too bad I didn’t find out sooner.
I started collecting newspapers about 2-3 years ago. Originally I collected US coins and baseball cards but transitioned to picture postcards from the early 1900’s. I wanted to go back further in time so I started to collect letters/stampless letters from the 1800’s including a few neat letters from the Civil War. In my quest to find earlier documents I stumbled upon your rarenewspaper website. I was amazed that newspapers could be had from the 1600/1700’s. Too bad I didn’t find out sooner.
 My favorite era is newspapers from the Revolutionary War and the early formation of the United States government. Friends and relatives are amazed when I show them a newspaper with George Washington’s name in it. A few of the papers have names of officers who were engaged in the Revolutionary war. To me that makes it very historical since I know an active participant actually read that paper.
My favorite era is newspapers from the Revolutionary War and the early formation of the United States government. Friends and relatives are amazed when I show them a newspaper with George Washington’s name in it. A few of the papers have names of officers who were engaged in the Revolutionary war. To me that makes it very historical since I know an active participant actually read that paper.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Thanks for sharing your story Dave. If you would like to share your story of how you became interested in collecting rare and/or historic newspapers, e-mail it to guy@rarenewspapers.com and place “My Story” in the subject field. Although not necessary, feel free to include an image. Please do not include your e-mail address or a personal website as part of the text of your story. We will post collector stories every few weeks and will send you a notice when your story appears. Thank you for your contribution to the community.
Number of titles, and where held…
August 17, 2009 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
 A four page promotional piece announcing the completion of a 30 year project titled: “History and Bibliography of American Newspapers 1690 – 1820”, now commonly referred to simply as “Brigham”, its creator, includes some statistical information which might be of interest.
A four page promotional piece announcing the completion of a 30 year project titled: “History and Bibliography of American Newspapers 1690 – 1820”, now commonly referred to simply as “Brigham”, its creator, includes some statistical information which might be of interest.
Brigham notes that from 1690 to 1820, there were 2120 different newspapers published. Of this totals the six New England states had 447; the six middle Atlantic states from New York to Maryland had 1023; the ten Southern states from Virginia to Louisiana had 425; and the seven Western states had 225. The city which from the beginning to 1820 had the most newspaper was New York with 138, followed by Philadelphia with 107, and Boston with 73.
Also, the six largest collections of newspapers before 1820 are:
1)American Antiquarian Society with 1492 titles
2) Library of Congress with 936 titles
3) Harvard with 732 titles
4) New York Historical Society with 634 titles
5) New York Public Library with 480 titles
6) Wisconsin Historical Society with 415 titles
Not quite a portable hairdryer…
August 15, 2009 by TimHughes · 1 Comment
 So how would you like to pack this hairdryer in the suitcase for a weekend trip? It might have been a great devise in 1900 but I’m sure it didn’t travel well. This ad appeared in the “Ladies’ Home Journal” issue of August, 1900.
So how would you like to pack this hairdryer in the suitcase for a weekend trip? It might have been a great devise in 1900 but I’m sure it didn’t travel well. This ad appeared in the “Ladies’ Home Journal” issue of August, 1900.
How to be a cowboy: The protocol in 1882…
August 13, 2009 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
 It’s interesting how the stereotype of the cowboy as created by Western movies and the lore generated by Western writers can hold true to reality. This was my thought when I can across an interesting tidbit from a Yuma, Arizona, newspaper of January 7, 1882—from a truly Western town at the high point of the Wild West era:
It’s interesting how the stereotype of the cowboy as created by Western movies and the lore generated by Western writers can hold true to reality. This was my thought when I can across an interesting tidbit from a Yuma, Arizona, newspaper of January 7, 1882—from a truly Western town at the high point of the Wild West era:
“He Wanted to be a Cowboy”
A youth recently went all the way from Chicago to New Mexico to become a cowboy. When there he explained his desire to a typical mountaineer whom he met and asked for instructions in the role he had wished to assume. Grasping him by the hand the mountaineer said: “You want to get a buckskin suit with plenty of fringe, a pair of high boots and a pair of high spurs. Then you want to get a broad-rimmed hat–the broader the better; two fort-fives, a knife, a Winchester rifle and a horse; then you want to get drunk and get on your horse; then take the reins in your teeth, a revolver in each hand, and go down the street at a full run, shooting at every jump. then come back and yell as loud as you can: ‘My name is ______ and I’m stinking for a fight; I’m a sone-of-a-gun from the plains.’ After that you will be a cowboy.” The picture is duly referred to the cowboy’s prototype in Western Missouri.”


