1776-2026: The Dream Still Shines at Dawn’s Early Light!
January 5, 2026 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
Whether we call it the Semiquincentennial, America250, the Quarter Millennial, the Sestercentennial, or simply the 250th birthday of the boldest experiment in self-government, 2026 rises like a new dawn—filled with promise, reflection, and hope for every American and every friend of liberty across the world.
The front page below, taken from a newspaper celebrating the Centennial Fourth of July in 1876, carries us back to that earlier moment of celebration—a time when a young nation looked proudly to its past and eagerly toward its future. It reminds us of the countless generations whose courage and sacrifices made possible Franklin D. Roosevelt’s enduring truth:
“We are a nation of many nationalities, many races, many religions—bound together by a single unity, the unity of freedom and equality.”
That vision still lights our way. Yet we are also called to remember Frederick Douglass’s wise and urgent reminder, spoken on the 23rd anniversary of emancipation in the District of Columbia:
“The life of the nation is secure only while the nation is honest, truthful and virtuous.”
As we celebrate this extraordinary milestone, may we lift our hearts in gratitude for the Divine grace that has guided us through triumph and trial alike. And as we look ahead, may we renew our shared promise—to preserve every hard-won freedom and to keep lifting the banner of justice, opportunity, and dignity for all who call this land home.
Here’s to the journey still unfolding. Here’s to the dream still alive.
Happy 250th, America!
Popcorn, Principle, and the Presidency: JFK’s Quiet Stand for Artistic Courage…
December 22, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
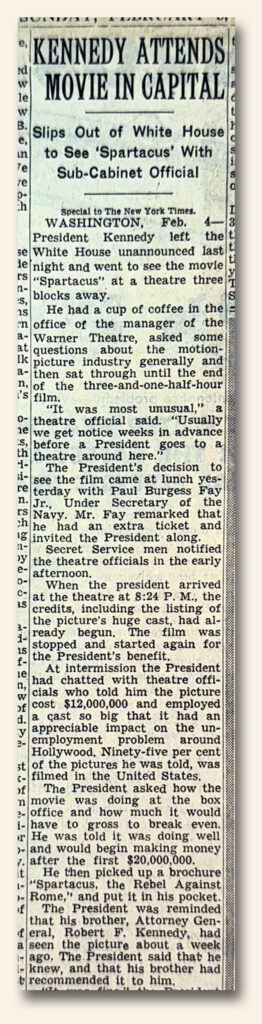 One of the many ways we build our database of key issues comes by way of requests from collectors? Case in point: A client recently asked if we had the February 5, 1961 issue of The New York Times which contained an inside report about President John F. Kennedy attending a movie at a local, D.C., public theater. Could such a report be significant; perhaps even collection-worthy? I immediately turned to the internet to see what I could find regarding this seemingly innocuous event. The following is a summary of what I discovered:
One of the many ways we build our database of key issues comes by way of requests from collectors? Case in point: A client recently asked if we had the February 5, 1961 issue of The New York Times which contained an inside report about President John F. Kennedy attending a movie at a local, D.C., public theater. Could such a report be significant; perhaps even collection-worthy? I immediately turned to the internet to see what I could find regarding this seemingly innocuous event. The following is a summary of what I discovered:
From the Silver Screen to the Oval Office: JFK’s Movie Night That Cracked the Blacklist
On February 3, 1961, just weeks after his inauguration, President John F. Kennedy quietly attended a screening of Spartacus at Washington, D.C.’s Warner Theatre. It may have looked like a simple night at the movies, but the moment carried deep cultural significance—marking the beginning of the end for Hollywood’s infamous blacklist.
At the heart of the story was screenwriter Dalton Trumbo, one of the “Hollywood Ten,” who had been blacklisted during the McCarthy era for refusing to testify before Congress. For years, Trumbo wrote under assumed names, but Spartacus producer Kirk Douglas decided it was time to credit him openly, defying industry fear and government pressure.
Kennedy knew exactly what that meant. By attending the film—and later praising it—he effectively gave a presidential nod to artistic freedom and to those silenced by the Red Scare. That quiet gesture helped dismantle a decade of fear and restored a measure of integrity to Hollywood.
Symbolically, Spartacus’s story of rebellion and freedom echoed the challenges Kennedy himself would face in a world divided by the Cold War and rising civil rights tensions. What began as a night at the movies became a turning point in America’s cultural history—proof that sometimes the most powerful stands for freedom don’t happen on the battlefield, but in the back row of a darkened theater.
So the question remains: Is this newspaper collection-worthy? My vote is yes, but such a call is certainly subjective.

Holiday Newsletter (2025) – Timothy Hughes Rare & Early Newspapers…
December 15, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
| Welcome to the Holiday Newsletter from Rare & Early Newspapers. Whereas a number of interesting items are included below, don’t miss out on one of our posts from a few years ago: “Yes, Virginia, there is a Santa Claus“.
This month’s highlights: 1) Newly Listed Catalog Items – The list of items which have been added to our most recent catalog after it went to print continues to grow – including a number of great (highly collectible) issues. These new listings may be viewed at: NEWLY ADDED CATALOG ITEMS 2) Discounted Issues (50% off): 100+ items have been added to last month’s list of discounted issues – each discounted by 50% (as shown) through January 15, 2026! Take a look; you won’t be disappointed: DISCOUNTED ITEMS (50% off) 3) Catalog 361 – Wonderful items from the December catalog still a remain. The available issues may be viewed at: CATALOG 361 4) Holiday-themed content – over 80 collectible newspapers with a Christmas, Hanukkah, or New Year’s theme are available at: ISSUES w/ HOLIDAY-THEMED CONTENT (you may need to view the full description if the “holiday content” is secondary to an historic report) 5) Additional Ideas for Gift Giving:
* Note re: Holiday Shipping – We are sending this newsletter a bit earlier than usual to increase the chance that any item/s ordered will arrive in time for Christmas. If historic/rare newspapers are part of your gifting plans this year, please know we will make every effort to ship incoming orders within 48 business hours. 6) The History’s Newsstand Blog – bi-weekly posts of potential interest to those who collect rare & early newspapers. An aye aye lemur’s handful of recent posts includes:
|
|
Thomas Jefferson helps to codify George Washington’s footsteps…
December 12, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
When it comes to collecting rare and early newspapers, those containing the text of presidential annual messages are quite desirable. While a handful are well known (Lincoln’s 2nd annual address, Washington’s 1st, Kennedy’s 1st, etc.), others fly well under the radar. A recently discovered broadsheet (Republican Argus, Extra, Oct. 16, 1808), containing Thomas Jefferson’s final address in 1808 brought this latter group to mind, yet, upon analysis in light of current events, seems to hold its own historically. The summary below, modified from multiple AI sources, is provided so you can draw your own conclusion. Enjoy.

Thomas Jefferson’s Eighth Annual Message to Congress, delivered on November 8, 1808, came at the close of his presidency during a time of international conflict and domestic unrest. He used the address to defend the Embargo Act of 1807, which aimed to protect U.S. neutrality and avoid war with Britain and France by halting foreign trade. Despite its economic toll on American farmers and merchants, Jefferson maintained that economic pressure was preferable to military conflict. The speech also reflected ongoing foreign policy tensions, particularly regarding maritime rights, and the young republic’s efforts to uphold sovereignty amid European aggression.
Jefferson’s speech highlighted the challenges of maintaining neutrality, the importance of strengthening U.S. military defenses, and his vision for internal development, including peace through trade with Native American tribes. It also revealed the political friction of the time, with Jefferson facing criticism from both Federalists and members of his own party over the embargo and proposed federal infrastructure projects. This period of political division underscored deeper questions about the role and limits of federal power in a republic still defining itself.
Most significantly, Jefferson’s 1808 address signaled the end of his presidency and affirmed his decision not to seek a third term. Although he had announced this publicly in 1807, his final annual message served as a symbolic and practical demonstration of his commitment to republican principles. By following George Washington’s example, Jefferson helped establish the precedent that presidents should serve no more than two terms. This voluntary transfer of power reinforced the principle that no individual should hold executive power indefinitely, a safeguard essential to American democracy.
Jefferson’s choice not to pursue a third term, especially during a time of national strain, cemented a critical political norm that influenced every president until Franklin D. Roosevelt. The importance of this precedent lies in its protection against the concentration of power and its promotion of leadership rotation—core values in a constitutional republic. Jefferson’s 1808 address, then, is not just a reflection on policy but a foundational moment in American political tradition, ultimately leading to the formalization of the two-term limit through the 22nd Amendment.
The December, 2025 Catalog (#361): Must-Have Newspapers for the 250th Anniversary of American Independence (1776–2026)
December 6, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
 As the United States approaches its semiquincentennial in 2026, collectors, museums, and history lovers are hunting for the most evocative newspapers from the Revolutionary era. This month’s RareNewspapers.com catalog is packed with exactly those treasures—original issues that let you hold the birth of the nation in your hands. Here are the top standouts that speak directly to the 250th anniversary celebration:
As the United States approaches its semiquincentennial in 2026, collectors, museums, and history lovers are hunting for the most evocative newspapers from the Revolutionary era. This month’s RareNewspapers.com catalog is packed with exactly those treasures—original issues that let you hold the birth of the nation in your hands. Here are the top standouts that speak directly to the 250th anniversary celebration:
1. #703265 – Massachusetts Centinel, Boston, January 16, 1788 – $5,885
The iconic “Federal Edifice” pillar cartoon showing the 11 ratified states holding up the new Constitution. One of the most famous visual celebrations of the successful Revolution and the founding of the permanent United States government.
2. #687284 – Norwich Packet, Connecticut, December 18, 1783 – $4,275
George Washington’s emotional farewell to his officers at Fraunces Tavern – the moment the Commander-in-Chief resigned his commission and returned power to the people. A perfect “end of the Revolution” companion piece for 2026 displays.
3. #718898 – The Cape-Fear Mercury, Wilmington, North Carolina, June 3, 1775 – $3,995
A rare (and intriguingly forged) Southern colonial newspaper from just weeks after Lexington & Concord. One of the scarcest North Carolina titles from the fateful year 1775.
4. #703479 – The Pennsylvania Gazette, Philadelphia, August 2, 1753 – $3,925
With Benjamin Franklin’s own imprint in the masthead. Franklin, the ultimate Founding Father, printed this very newspaper—making it an ideal pre-Revolutionary artifact leading into the 250th.
5. #703307 – Connecticut Courant, Hartford, February 10, 1777 – $1,485
Prints more than half of Thomas Paine’s legendary “American Crisis” Number 2 (“These are the times that try men’s souls…”). Paine’s words kept the Revolution alive during its darkest winter.
6. #703299 – New-England Chronicle, Cambridge, January 4, 1776 – $895
Major General Charles Lee’s fiery open letter to British General Burgoyne, plus the exposure of Dr. Benjamin Church’s traitorous letter to the British—the first known act of American espionage.
7. #701110 – Boston Gazette & Country Journal, July 9, 1770 – $975
Paul Revere’s famous patriotic masthead engraving of Liberty releasing the dove of peace, combined with fiery coverage of the Non-Importation Agreement in the wake of the Boston Massacre. Pure 1770 resistance spirit.
Also noteworthy in the Revolutionary-era spotlight this month:
• The definitive three-day Battle of Gettysburg coverage is stunning (#705943), but for the 250th focus, the issues above are the true headliners.
If you or your institution are building a 2026 exhibit, creating a museum-quality timeline, or simply want to own the actual newsprint read by Patriots 250 years ago, what remains from the above are viewable HERE.
Which one will be the centerpiece of your America 250 collection? Let us know in the comments!
Lead-up to a Nation… as reported in the newspapers of the day (November, 1775)…
December 5, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment

Continental Currency – No Power to Tax or Regulate (Lead-up to a Nation – E14)
League of Friendship-Articles of Confederation Underscored National Power (Lead-up to a Nation-E15)
James Rivington – From Impartial to Loyalist (Lead-up to a Nation – E16)
The Liberty Bell – Proclaim Liberty Through the Land (Lead-up to a Nation – E17)
We hope you are enjoying this year-long trek to the 250th anniversary of The United States through the eyes of those who were fully engaged, first hand. As mentioned previously, all accounts are rooted in what they read in the newspapers of the day.
“History is never more fascinating than when read from the day it was first reported.” (Timothy Hughes, 1975)
Announcing: Catalog #361 for December, 2025 – Rare & Early Newspapers…
December 1, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
|
|
Properly Directed Thankfulness – George Washington and the Foundations of a New Nation…
November 25, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
On October 3, 1789, just months into his presidency, George Washington issued the very first official presidential proclamation. Fittingly, his choice of subject set the tone for a new nation: a call for a national day of thanksgiving and prayer. In it, Washington urged the people of the United States to acknowledge “with grateful hearts the many signal favors of Almighty God, especially by affording them an opportunity peaceably to establish a form of government for their safety and happiness.” This was more than a holiday declaration—it was a reminder that gratitude, humility, and faith would form part of the nation’s foundation.
Below is the complete text of Washington’s Thanksgiving Proclamation as it appeared on the front page of the Gazette of the United States on October 7, 1789:

November Newsletter (2025) – Timothy Hughes Rare & Early Newspapers…
November 14, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · Leave a Comment
|
|
Who’s Who in Newspapers – John Wanamaker edition
November 10, 2025 by GuyHeilenman · 1 Comment
Typically, our “Who’s Who in Newspapers” series highlights individuals who were unfamiliar to me before I delved into the world of Rare & Early Newspapers. Today’s post is a departure from that norm. While reviewing the December 12, 1922, issue of The Bethlehem Times, I came across a front-page report of John Wanamaker’s passing. The article stirred a flood of childhood memories tied to this remarkable man whose legacy left a lasting impression on me. Eager to share his story, I hope the following introduction sheds light on his extraordinary contributions.
John Wanamaker: The Merchant Who Made Shopping an Experience
 From personal memories to retail innovation, Wanamaker’s left a legacy that reshaped both commerce and tradition. Every December starting in the mid-1950s, my parents bundled up my siblings and me for a trip into Philadelphia to see the Christmas light and music show at Wanamaker’s (currently being converted into a mixed-use facility). To us, it was pure magic — thousands of twinkling lights, the sound of the great pipe organ, and crowds of families gathered in awe. With my grandmother working in the store during those years, Wanamaker’s always felt like more than a department store — it felt like part of our family’s story.
From personal memories to retail innovation, Wanamaker’s left a legacy that reshaped both commerce and tradition. Every December starting in the mid-1950s, my parents bundled up my siblings and me for a trip into Philadelphia to see the Christmas light and music show at Wanamaker’s (currently being converted into a mixed-use facility). To us, it was pure magic — thousands of twinkling lights, the sound of the great pipe organ, and crowds of families gathered in awe. With my grandmother working in the store during those years, Wanamaker’s always felt like more than a department store — it felt like part of our family’s story.
That sense of wonder was no accident. John Wanamaker (1838–1922), the man behind the store, believed shopping could be more than a transaction — it could be an experience. When he opened his Philadelphia department store in 1876, it quickly became a model for modern retail. Wanamaker pioneered the one-price system (no haggling), introduced the money-back guarantee, and used newspaper advertising on a scale few had seen before.
He also reshaped how Americans paid for what they bought. Realizing that many working families couldn’t afford to pay cash for larger purchases, Wanamaker offered installment plans and charge accounts. This bold move laid the foundation for consumer credit, opening the door for more households to access quality goods.
Beyond retail, Wanamaker served as U.S. Postmaster General under President Benjamin Harrison, introducing commemorative stamps and expanding rural mail delivery. Yet it was his Philadelphia store — both marketplace and civic landmark — that became his greatest legacy.
Even today, the memory of standing with my siblings beneath the glow of the light show while the Wanamaker organ thundered through the Grand Court remains a vivid reminder of how one man’s vision reshaped not just shopping, but tradition itself.
Wanamaker’s Firsts – Innovations that reshaped retail
- One-Price System – Ended the practice of haggling; everyone paid the same fair price.
- Money-Back Guarantee – Built customer trust and loyalty.
- Large-Scale Advertising – One of the first to use newspapers to reach wide audiences.
- Department Store Experience – Turned shopping into a cultural outing with art, music, and public events.
- Consumer Credit – Introduced installment plans and charge accounts, paving the way for modern credit.





