Period printing… Did you ever notice…?
April 30, 2012 by GuyHeilenman · 1 Comment
A few months ago we received an inquiry from one of our friends wondering why pre-1900 newspapers included a period after the newspaper’s title in the masthead. While I hold hundreds of such issues in my hands each week, I had never taken notice of this. Wondering if this was in fact the case, I quickly began searching through our 19th and 18th century archives, and low and behold, every title ended with a period. Searching through our 20th century inventory I discovered that none of the issues did. I asked Tim Hughes his thoughts on the matter, and his response was as follows:
Regarding the query about periods at the end of 19th century titles, I don’t believere there is a reason beyond it simply being the grammatical style of the  period. In fact the practice goes back to the 17th and 18th centuries as well. It was just the way newspapers (and magazines) were laid out, perhaps following some sort of grammatical “rule” of the day. There was also–compared to today–an excessive use of commas within text, which again was just the style of the day.
period. In fact the practice goes back to the 17th and 18th centuries as well. It was just the way newspapers (and magazines) were laid out, perhaps following some sort of grammatical “rule” of the day. There was also–compared to today–an excessive use of commas within text, which again was just the style of the day.
Perhaps the more interesting question would be when & why was the period eliminated at some point in the 20th century? I would suspect one paper just made the decision and everyone else eventually followed, as there was much competition and copying among newspapers. Sorry I don’t have a more intriguing answer!
If any of our readers have additional information in regards to this, feel free to respond.
Colonial newspaper founded by a woman… A rare find…
October 31, 2011 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
A recent collection which came into our inventory included a rare title which didn’t strike me until I looked more closely.
 “Salem Gazette” is a somewhat common from the 18th century so I wasn’t surprised to see the title when quickly examining the collection. But then I noticed the date from the Revolutionary War, which I thought odd. Upon investigation I found there were actually four different newspapers titled “Salem Gazette“, one from 1774-1775, one from 1781-85, and one from 1790 thru the 19th century. These latter two are were quite familiar to me, but our issue was yet a fourth title, one which I had never encountered in 35 years, and this one lasted but 36 issues during the year 1781. But of greater significance was that the masthead noted it was published by a woman, Mary Crouch. See the hyperlink for much more on her fascinating life, but suffice it to say she was no stranger to publishing a newspaper as she had much experience in South Carolina.
“Salem Gazette” is a somewhat common from the 18th century so I wasn’t surprised to see the title when quickly examining the collection. But then I noticed the date from the Revolutionary War, which I thought odd. Upon investigation I found there were actually four different newspapers titled “Salem Gazette“, one from 1774-1775, one from 1781-85, and one from 1790 thru the 19th century. These latter two are were quite familiar to me, but our issue was yet a fourth title, one which I had never encountered in 35 years, and this one lasted but 36 issues during the year 1781. But of greater significance was that the masthead noted it was published by a woman, Mary Crouch. See the hyperlink for much more on her fascinating life, but suffice it to say she was no stranger to publishing a newspaper as she had much experience in South Carolina.
The hyperlinked article mentions she took over the publication of her husband’s (Charles) “South Carolina Gazette” after he died in 1772. She then began her own newspaper, the “Charlestown Gazette“, in August of 1778. When the British occupied her town in 1780, being a staunch patriot, she moved north to Salem, Massachusetts, where she began publishing this “Salem Gazette” in 1781. The number we have is dated February 6, 1781 and is issue number 6 of the 36 published (see the hyperlink). Relatively few institutions hold any issues of this title, and only four issues of this date are held by institutions.
There were a number of women who published newspapers in the 18th century & virtually all that I could discover did so by continuing a printing business upon the demise of their respective husbands. One exception was Mary Goddard who published the “Maryland Journal” during her brother’s absence from 1774-1783. But Anne Catherine Green took over her late husband’s “Maryland Gazette” upon his death in 1767; Hannah Watson took over her husband’s (Ebenezer) “Connecticut Courant” upon his death in 1777; Margaret Draper took over the “Massachusetts Gazette” upon the death of her husband Richard in 1774; Clementine Rind took over “The Virginia Gazette” in 1773 when her husband William died; and Ann Franklin published the “Newport Mercury” upon the death of her son James in 1762. I am sure there are others as well.
From what I could determine Mary Crouch may well be the first American woman to create a newspaper, and she did so twice. Her first being the “Charlestown Gazette” and her second the “Salem Gazette“. Any research to the contrary would be gratefully received and shared with our fellow collectors.
War makes “sad havoc” among the newspapers…
April 2, 2011 by TimHughes · Leave a Comment
This item provides some interesting facts on what war does to newspaper publishing. It appeared in the “Daily Richmond Examiner” issue of February 4, 1864.
More on printing newspapers in the 1700’s…
August 24, 2009 by TimHughes · 3 Comments
This article is primarily taken from the April, 1996 edition of “Collectible Newspapers” edited by Rick Brown, whom we thank for this contribution. It offers some interesting insights into the printing & distributing of newspapers in the colonial and post-colonial era of the United States.
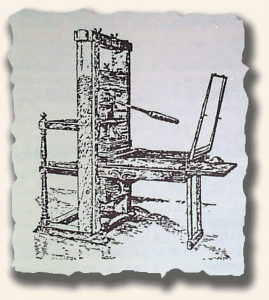 Newspapers from the latter half of the 18th century were relatively scarce. One factor was that early settlers were busy clearing the land & otherwise making the land habitable & sustaining. Plus only a small percentage of the population had reading skills beyond that of the basic rudiments. Although most towns of any size by 1715 had tracts of land set aside for schools, few actually had schools built & in operation.
Newspapers from the latter half of the 18th century were relatively scarce. One factor was that early settlers were busy clearing the land & otherwise making the land habitable & sustaining. Plus only a small percentage of the population had reading skills beyond that of the basic rudiments. Although most towns of any size by 1715 had tracts of land set aside for schools, few actually had schools built & in operation.
Nearly all 18th century newspapers were edited & published by printers that had a general printing business and also printed pamphlets, books, broadsides, lottery tickets, etc. Many also sold merchandise, groceries, patent medicines, and a variety of other goods. Rags, which were used to make the paper , were scarce in the colonies so most of the paper was imported from England.
Newspapers were printed on wooden hand presses with each applicatoin of ink to paper requiring a pull of by lever and screw. It was not until around 1816 that the new iron Columbian press came into general use. Instead of a screw it used a series of compound levers that multiplied the pull of the operator. But still, all hand presses were slow & laborious. The forms had to be laid by hand and the ink was poor and of uneven quality. Types were frequently old and worn.
After the newspapers were printed, distribution difficulties were encountered. Circulation was confined, for the most part, to the towns in which they were published. They were distributed to the rural areas by postboys on horseback and by stagecoach drivers. The roads were bad & the postal system was slow. Subscribers were few & the cost of an issue relatively expensive so newspapers were typically handed around from one to another so that a single copy was ready by many. Even those who subscribed often failed to pay for their subscriptions.
It has been estimated that the largest circulation of a single newspaper during the earlier colonial period was about 350 and that only a few reached this high of a number of circulation. By the 1750’s circulation for larger city newspapers reached upwards of 600 of each issue printed and during the Revolutionary War some newspapers boasted circulations in excess of 2000. By 1790 most newspapers were printing less than 1000 copies but the very popular “Columbian Centinel” from Boston was printing over 4000 copies of each printing date.
Despite poor equipment, limited circulation, nonpaying subscribers, poor distribution facilities & the general unprofitability of publishing a newspaper, the number of newspapers being published continued to increase as the years went by. There were numerous failures, but new newspapers were established to replace them. From 1704 to 1820 about 1634 newspapers came to life and died. Of that number only two-thirds of them lived beyond three years.




